Retail Meets VR: How Virtual Reality Is Shaping the Shopping Experience
Shopping is no longer confined to malls or apps. It’s stepping into immersive virtual worlds through Virtual Reality.

Content Map
More chaptersWhat images come into your head when you hear the word “shopping”? Is it walking around in a mall, entering and exiting one store after another? Or is it driving to a shiny boutique downtown? Or, perhaps you weren’t thinking about a physical, brick-and-mortar shopping experience, but rather an online one: turning on an e-commerce app and scrolling until you find your desired items and add them to your cart. Shopping has undergone drastic changes over the past two decades, and it is continuing to evolve.
One such innovation is the presence of Virtual Reality, or VR, in retail businesses. While VR is often associated with entertainment activities like gaming, it has proven to be an exciting addition in the retail world. This article aims to understand what VR in retail truly is, how it can benefit retail, why many businesses are still hesitant to adopt it, and how you can do so easily. Of course, we’ll also be examining real-life examples and see what we can learn from them.
Key Takeaways:
- Virtual reality (VR) is a technology that immerses users in interactive, computer-generated 3D environments, blending real-world movement with digital experiences.
- Using VR in retail boosts customer engagement and satisfaction and allows them to experience the product from the comfort of their own home. It is also a great tool for training employees in stressful situations.
- Even though VR has been applied in real-life brands like IKEA and Puma, its adoption rate is still slow due to high costs, complex implementation and mixed feedback from customers.
- To fully integrate VR in retail businesses, you need to have a clear vision of how the tech is going to be used, research your audience and competitors thoroughly and finally, consult with professionals to build an app that meets your unique needs.
Understanding Virtual Reality in the Retail Industry
What is Virtual Reality (VR)?
Virtual reality (VR) is a technology that creates a computer-generated, three-dimensional environment that allows users to immerse themselves in and interact in real time. Using devices like headsets, gloves, or sensors, VR translates a person’s movements into the virtual space, making the experience feel realistic and responsive. These environments can be built from real-world imagery or entirely through computer graphics, allowing people to explore everything from simulated workplaces to fantastical worlds, or even interconnected spaces like the Metaverse.
How Does VR Work?
Simply put, VR replaces the real-world environment with a realistic 3D environment. To create the most immersive experience and ensure that the virtual world resembles its natural environment as closely as possible, the tech utilizes AI algorithms and machine learning (ML).
AI and ML project new elements onto a mathematically calculated surface. They enhance graphics rendering, provide a more natural and personalized user experience, all while tracking real-world objects.
Sometimes, the terms Augmented Reality (AR) and VR are used interchangeably. This isn’t entirely correct, as VR and AR are significantly different. VR replaces the real-world environment with a virtual one, but AR only adds or overlays digital elements onto the real world.
Benefits of VR in Retail
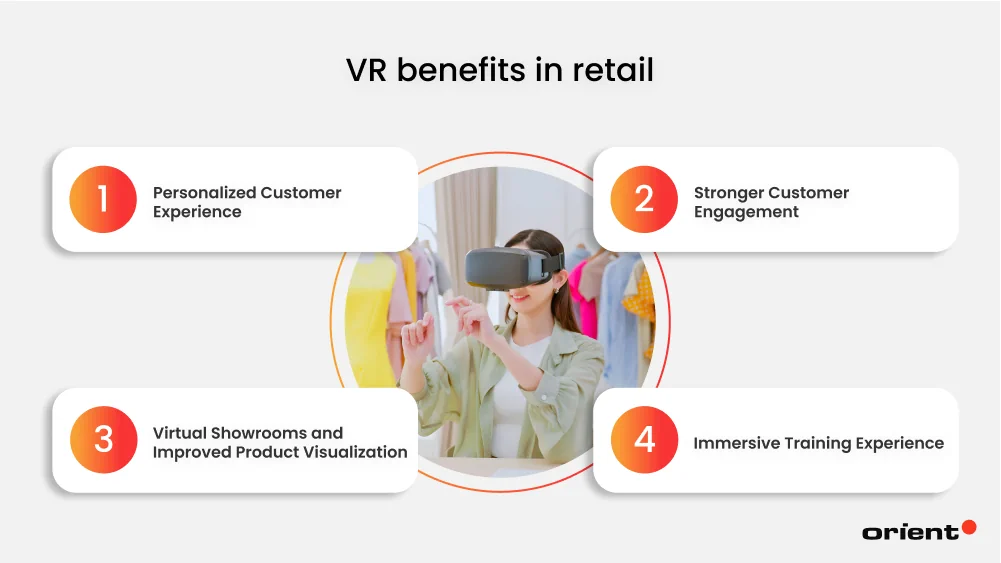
With the power to collide the real world with the virtual one, VR is slowly but surely reshaping the retail sector, whether it involves marketing, customer engagement, or innovative customer experiences.
Personalized Customer Experience
Most businesses collect a large amount of data to identify patterns, customer preferences, and forecast trends. Such data can also be utilized to create personalized, immersive VR experiences, such as customized product recommendations. Making customers feel valued and cared for is how you build loyalty, retain existing buyers, and differentiate yourself from competitors.
Stronger Customer Engagement
Investing properly in customer engagement fosters a strong relationship with your buyers beyond purchases. Facilitating quality engagement with customers is how you build a strong emotional connection with them, keep your hard-won members, and most important of all, keep your brand at the top of their mind.
There are plenty of ways to engage customers, but make sure you don’t overlook VR or AR. Customers can experience your services and products, even from the comfort of their homes, with VR and AR.
Virtual Showrooms and Improved Product Visualization
Today’s retail landscape no longer considers brick-and-mortar stores a must-have. Online-only shops have become more and more common. While this retail mode saves costs on rent and maintenance, it does limit customer interaction with the product.
With VR technologies, this concern will be significantly reduced. You can create a virtual showroom with an immersive environment, where customers can experience the product for a more confident and informed purchase decision. Ensuring a consistent VR experience can also boost conversion rates and ultimately boost online sales.
Immersive Training Experience
VR plays a significant role in reshaping the customer experience within a business. However, it can also reshape experiences within the retail company, which in this case, is training employees.
Training staff with immersive VR technologies allows businesses to accurately assess the ability to perform the job while also giving the trainee a chance to experience the stress in real-life situations.
In a VR training session, for example, new employees are asked to deal with an angry customer or trained to handle long lines of customers during peak seasons like Black Friday or Christmas.
Why VR Adoption in Retail Is Still Slow
The size of the worldwide virtual reality (VR) market was assessed at USD 59.96 billion in 2022 and is expected to increase at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27.5% from 2023 to 2030, reaching USD 435.36 billion, according to Grand View Research. The estimated number of VR users in the US alone in 2024 is 77 million people, an 8% increase from 2023.
Even with such impressive numbers, there is still a lot of hesitation around the adoption of this tech. In many businesses, the tech is still only used in small-scale, pilot test projects. The Virtual and Augmented Reality Adoption Trends and Customer Experience 2024 reported that the use of VR and AR is currently limited, and investment is low, though satisfaction among users is reasonable. However, organizations that have adopted these technologies are seeing significant financial benefits: many recoup their investment within two years, and most stay on or under budget for setup and ongoing costs.
Why do such challenges persist within the VR/AR realm? The following reasons might explain the tech’s slow adoption rate.
High Upfront Investment
Despite VR’s continuous evolution, it is still among the more expensive technologies. Several factors contribute to the high numbers:
- Complex hardware. VR experiences come with a headset, but that’s only the beginning. The key to a VR system involves numerous tracking sensors like accelerometers and gyroscopes. HMDs incorporate high-resolution displays, lenses for wide views, and real-time stereoscopic 3D graphics. To ensure the smoothest experience possible, manufacturers need to use expensive display components, e.g., OLED or AMOLED. These requirements lead to a need for a powerful GPU to render high-quality 3D graphics in real-time, handle AI and ML algorithms, and other tracking, sensors, and audio systems.
- VR application development. VR and AR need specific software development kits to develop apps that produce such immersive and unique experiences. These tools come with licensing or subscription fees, but that’s not the most costly part yet. Developing VR apps requires time and significant human resources – a 3D modeler, cross-platform development capabilities, and a team with design and animation capabilities.
- Economy of scale. Unlike other electronics, VR has not yet become a mainstream device to benefit from mass production. The complex hardware, long development and research hours still keep its costs high, despite VR tech reaching beyond the gaming industry and being applied in other fields.
Complex Implementation
Implementing VR is no easy feat. While we do wish it were as simple as plugging the device in and using it, the setup and implementation are long and sometimes frustrating. A few examples of the integration process include:
- System integration. VR systems must connect seamlessly with product databases, inventory and fulfillment engines, and mobile/web applications.
- Cross-platform performance. The VR experience needs to be smooth and intuitive across different devices and operating systems, from iOS and Android to desktop platforms.
- User experience consistency. Delivering a reliable and engaging interaction is crucial. Users expect the same quality whether they do online shopping, use the VR headset in-store or on their mobile devices.
- Technology maturity gap: Many retailers are still working on basic improvements like mobile responsiveness and omnichannel consistency.
Mixed Consumer Reaction
It’s safe to say that the majority of users have not yet adapted to VR and AR technologies. Yes, millennials and Gen Z have shown interest in the tech and even actively use it in different settings, but it’s still only a small number of the population. Shopping is often viewed as a transactional activity – scan the aisles or online stores for the item, add it to the cart, then pay and leave. Virtual try-ons are interesting, but they won’t be considered a necessary part of a speedy shopping trip.
Real-Life Use Cases of VR in Retail
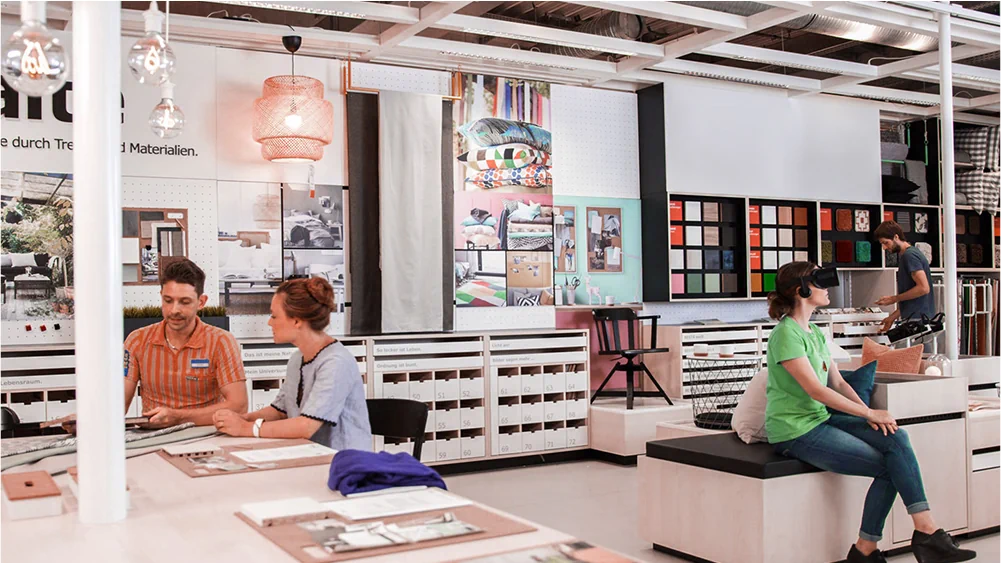

Even though there still exists a lot of friction for the application of VR in retail, it has been used in numerous real-life situations and has seen some encouraging levels of success.
IKEA’s Virtual Showrooms
IKEA launched IKEA Kreativ – a digital design space using a wide array of technology, including mixed realities, spatial computing, and machine learning.
This virtual showroom provides its users with a comprehensive 3D shopping experience, including:
- Exploring IKEA products in over 50 inspirational 3D showrooms.
- Designing and trying out products in lifelike spatial settings.
- Using IKEA Kreativ Scene Scanne to create editable 3D replicas of personal spaces.
- Using the IKEA App to ‘erase’ existing furniture, position new IKEA furnishings, and swap alternatives.
- Imagine a home life from anywhere by adding products to your cart, saving design ideas, and sharing them with family and friends.
The experience doesn’t end there. Customers’ virtual rooms are stored in the cloud, allowing for in-store shopping.
Puma’s Mixed-Reality Sneaker Shopping
Puma partnered with Meta to launch a mixed-reality shopping experience on Meta Quest headsets. Shoppers can explore a virtual storefront, interact with the new basketball shoe, and even measure their foot size using modern controllers. By blending physical and digital elements through WebXR, Puma is reimagining online shopping as an immersive, interactive experience that goes beyond traditional e-commerce.
VR Test Drives by Volvo
Volvo engineers use a VR-powered simulator featuring Varjo’s mixed-reality headset, Unity’s 3D platform, and a Teslasuit to test safety and autonomous driving features. Drivers can operate real cars on real roads while experiencing simulated traffic scenarios. This allows Volvo to test collision-avoidance technologies, study driver behavior, and accelerate innovation, all in a safe, cost-effective environment.
VR in Retail Education at the University of Arizona
Although this example is not directly related to how VR is applied in the retail industry, it shows how VR is used to understand and elevate the retail-related experiences. At the University of Arizona, retailing and consumer science students are learning how store design influences shopping behavior using a virtual “digital twin” of the Lundgren Consumer Science Lab.
Wearing VR headsets, students can walk through realistic virtual aisles, rearrange shelves, adjust product displays, and track shopper movements in real time. This immersive lab allows them to test merchandising strategies and analyze consumer behavior in ways that wouldn’t be possible in a traditional classroom. By blending real-world data with VR simulations, students gain hands-on experience with cutting-edge retail technology and gain practical skills to enter the ever-evolving retail industry.
How to Successfully Adopt VR in Retail

VR, along with AR and mixed realities, can be a tricky technology to get right. While we always advise consulting with experts in the field, like Orient Software, for the smoothest integration, here are fundamental steps for a successful VR adoption.
Identify VR Use Case
Start with a clear goal. Why did you decide to implement retail for your retail business? Are you using VR for:
- An enhanced visitor experience during special sales events?
- Training sales staff?
- For marketing purposes, where can you guide customers through digital catalogs and familiarize themselves with a product before they decide to close a deal?
Whatever your goal for using VR is, make sure to keep it at the forefront of every decision-making process.
Research the Target Audience and Competitors
After nailing down the key goals, try clarifying by identifying your target audience and competitors.
- Target Audience. Who are you building this for? Are you targeting in-store shoppers, online buyers, or both? Think about how they will engage with the VR experience. Will they come to your showroom, or access it via mobile app? The answers to these questions will influence how the project proceeds.
- Accessibility. What platforms should your VR experience support? Do you prioritize premium VR headsets or a more accessible experience through smartphones and web browsers? Remember, accessibility decisions can affect adoption rates.
- Competition. Research your competitors and how they are applying VR. Are they offering virtual try-ons, where consumers can try-before-you-buy, or do they mainly use VR for training? Understanding how your competitors use the tech can help you spot gaps and differentiate yourself from the rest.
Balance Experience and Cost
Not every VR project needs the same setup. If you’re running a campaign for the public, simple mobile-based headsets might do the job without breaking the budget. But if you’re building a long-term training tool for employees, higher-quality headsets with better resolution and interactivity can deliver stronger engagement and knowledge retention.
The key is to balance cost with quality. Affordable options already exist for short experiences, while premium headsets like Oculus or HTC Vive can create immersive, game-like environments for bigger projects. As the technology keeps evolving, VR doesn’t have to be out of reach; retailers can scale experiences to match both budget and audience needs.
Understand the Development Process
You might be carrying out the previous steps on your own, but at this stage, you’ll often need help from a professional VR development team. They will do most of the heavy lifting, but understanding the process helps you monitor and keep the project under control.
- Design: This stage gathers all the information, including requirements, ideas, research, and available resources. The UX team then creates the interface and tests it directly in the VR environment.
- Asset Creation: 3D elements bring the VR world to life. The team develops environments, objects, and visuals that shape the user’s experience.
- Start with an MVP: Rather than going all-in from the start, create a minimum viable product. It allows you to validate your idea early and reduce risk before scaling up.
- Carefully Calculate Costs: Factor in both development and hardware costs, as they can vary widely depending on quality and use case. Always align spending with your goals and expected ROI.
- Test, Review, Deploy: Extensive testing ensures the app runs smoothly and delivers on requirements. Only then should you launch it to your intended audience.
Last Note

The retail industry is always evolving, and that’s what makes it exciting. Embracing new technology isn’t just about staying current; it’s about creating joyful customer experiences and sustainably growing your business. At Orient Software, we’re passionate about helping you innovate with confidence and build for the future. Reach out to us today to elevate your retail business!






