Most people have a stereotypical image of robots like the one in Terminator (1984) or Ghost in the Shell. However, reality is far different. Unlike famous Hollywood humanoid characters, modern robots are mostly undramatic mechanical devices programmed to perform specific repetitive functions.

Nowadays, we interact with robots on a daily basis without noticing or calling them “robots” at all. What once firmly belonged in the realm of science fiction has now evolved and been steadily shaping modern lives. They are no longer just giant arms locked away on factory floors. They vacuum our rooms while we work, glide through restaurant floors to ferry food to tables, and roll through supermarket aisles to check for misplaced items or low-stock shelves.

Indeed, robots are now around us. We clearly see them in homes, restaurants, airports, or stores where they operate right in front of people. However, in other fields like hospitals, they work behind the scenes, so we can barely see them but still feel their presence.
Long story short, robotics has matured to the point where robots are no longer exotic, especially with the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning. They’ve become infrastructure, woven quietly into everyday environments, shifting from simple task automation to intelligent, adaptive support that fits naturally into the picture of life and business of modern people. Let’s take a closer look at the typical examples of robots in everyday life.
Beyond Sci-Fi: What Robots Can Really Do for Human Beings
When you strip away the hype, robots are never about replacing people with machines. They are about revolutionizing how humans work, live, and channel our efforts as well as resources to particular areas of daily life. Below are some of the most meaningful ways robots already create value in everyday life:
Safety
Robots act as a buffer between humans and harm. This is a human-centric way to leverage robotic equipment.

Robots can take on “dirty, dull, and dangerous” jobs that people should not have to handle when safer alternatives exist, such as bomb disposal, firefighting, or working with toxic substances. Also, they can carry out tasks in hazardous environments where it would be too risky, exhausting, or simply impossible for humans to operate for long. For example, robots can be sent into the inside of a nuclear power plant or the deep ocean, so humans don’t have to risk their lives.
Convenience & Time-Saving
Robots deliver convenience while optimizing time. They automate repetitive and arduous tasks, which helps reduce human effort. Beyond convenient gadgets for just automation, robots are powerful tools for reallocating time from low-value, low-satisfaction work to more meaningful activities.

Home robots like cooking bots, lawn-mowers, or vacuum cleaners can shave off routine household chores so people can make time for their priorities. For example, family, hobbies, or rest. In business environments, service robots act as assistants to automate the “in-between” work. For instance, shuttling items from point A to point B, queuing orders, or handling basic, repeatable steps in a process.
Productivity & Cost Reduction
Robots do not tire, get distracted, or vary in performance. They are capable of dramatically boosting productivity by working faster, longer, and with fewer breaks than humans. Also, they can lower the likelihood of human errors and speed up workflows. In a manufacturing environment, a robotic arm can assemble products with great precision all day long, leading to higher production speed and productivity.

Moreover, robots can be configured to optimize resource allocation, which enables them to deliver more output with the same or even fewer resources. Industries experiencing labor shortages or seasonal demand peaks can benefit from robots.
Accessibility & Independence
In a collaborative way, robots extend human potential by absorbing tasks that would be difficult or impossible for people to do on their own. You will notice this tangible benefit in healthcare and well-being. Assistive robots empower individuals, particularly older adults or those living with disabilities, to live more autonomously.
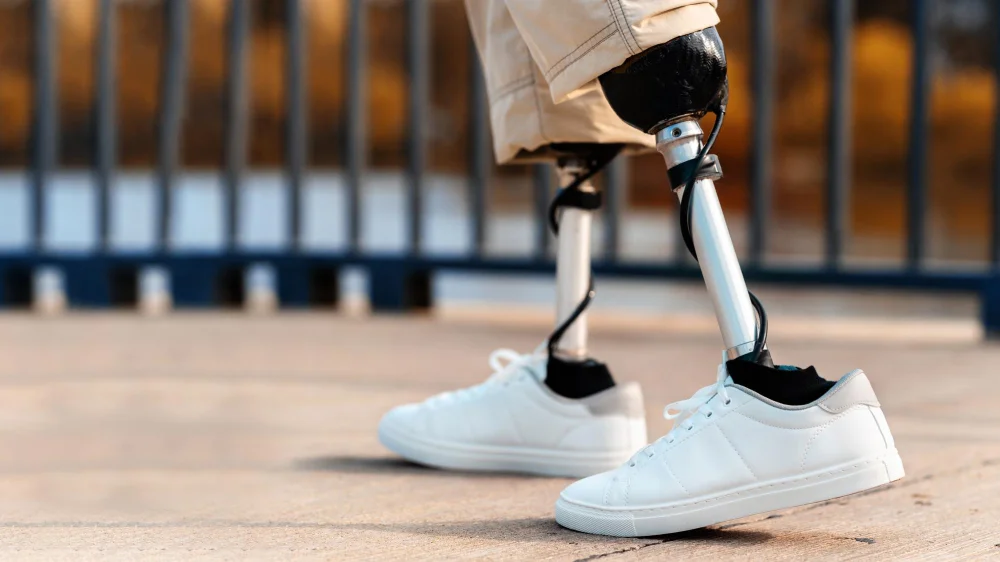

For example, robotic wheelchairs with navigation support, exoskeletons that help users stand or walk, and assistive arms that help with lifting heavy objects and other daily activities all broaden what individuals can do on their own.
Surveillance & Security
Security robots can be equipped with cameras, thermal sensors, and AI-based anomaly detection, providing a clear view into places that are inaccessible, hard to reach, or simply too dangerous for humans.

Robots act as eyes and ears on the front line. They enable scouting around larger areas and spotting anomalies without requiring the physical participation of humans. For example, a bomb disposal robot can roll into potentially explosive environments. Or, an inspection robot can enter collapsed buildings, tunnels, or contaminated areas.
Emotional & Social Support
The capabilities of robots coupled with machine intelligence have transcended improved operation and automation. There are some robotic companions created specifically to support emotional well-being and social interaction.

Such robots are designed to understand and exhibit emotions when interacting with humans or other systems. Some are already used in various practical, real-world settings like healthcare, education, customer service, and research. Meanwhile, continuous testing and experiments are going on for others.
Popular Use Cases of Robots in Human Life
In reality, robots already appear in more places than most people realize.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots): The Cooperative Partner
Unlike traditional industrial robots that are usually fenced off for safety and operate in isolation, cobots are engineered to work alongside humans in a shared workspace. Collaborative robots are built with sensors, lightweight designs, force limits, and intelligent control to slow down, stop, or adjust their motion when a person comes close. While human workers focus on delicate tasks, robotic partners take on repetitive and physically demanding jobs. The integration of collaborative robots reduces cognitive and physical strain, fosters a safer human-robot working environment, and democratizes automation.
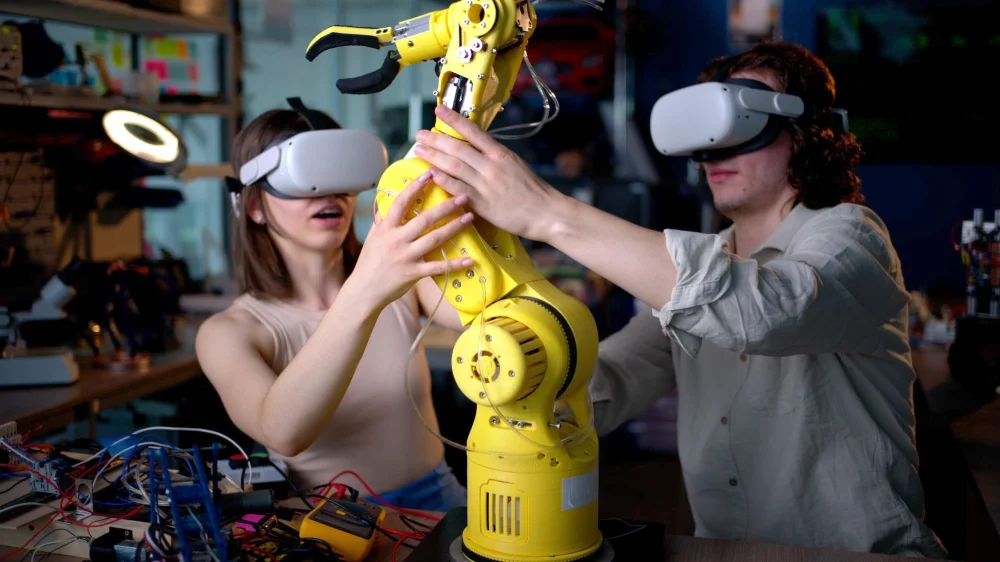

Cobots are often found in industrial settings like manufacturing and logistics. In factory or warehouse environments, these robotic partners take the form of articulated robotic arms mounted on workbenches, mobile bases, or production lines. They handle manual duties like assembly, screwdriving, machine tending, quality inspection, and packaging, or other heavy lifting activities.
In the age of AI, many modern cobots practice machine learning and utilize augmented intelligence to enhance precision and provide fully automated workflows. Cobots are still programmed to collaborate with humans, but the newer generations are designed to enable autonomy, capable of handling tasks with minimum supervision.
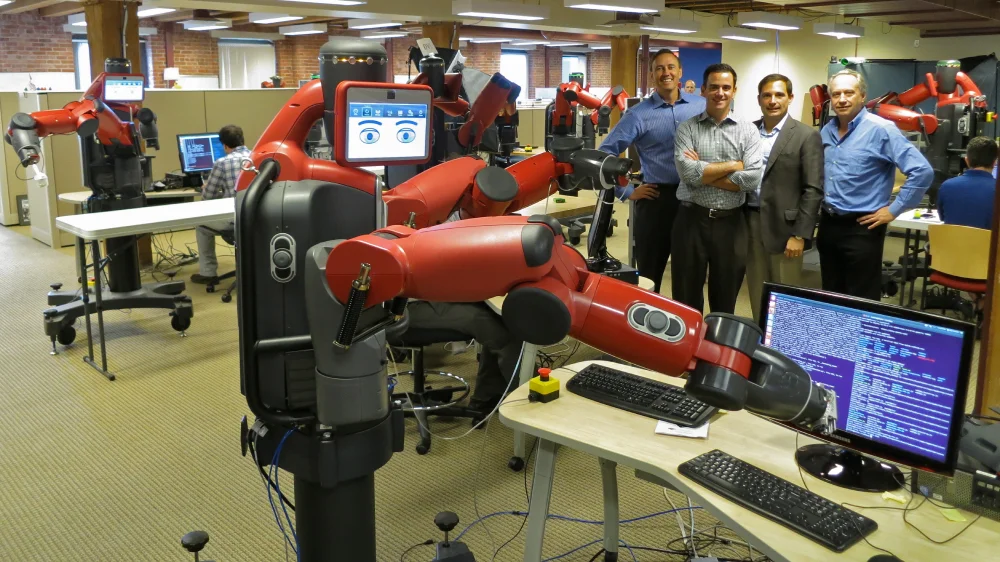

One of the widely recognized pioneers is a robot named Baxter. Developed by Rethink Robotics in 2012, Baxter is a two-armed model with an animated face. Baxter was designed for simple industrial jobs, such as loading, unloading, sorting, and material handling. Baxter was made approachable and easy to use, so operators can train it by physically guiding its arms, instead of complex programming. Even though Baxter was eventually shut down, its introduction marked the turning point of modern robotics.
At the current time, there are more cobots that transform workplaces and embody the principle of human-robot collaboration. For example, Universal Robots’ UR series, ABB’s YuMi, FANUC’s CRX, and KUKA’s LBR iiwa.
Domestic Robots: The Quiet Helper
This is a type of autonomous, programmable machine designed for household assistance in private or residential environments, such as homes, pools, gardens, etc. Therefore, domestic robots are also known as service bots or home robots. These “quite helpers” can perform a variety of mundane tasks in daily life, like cleaning, lawn mowing, looking after pet animals, pool maintenance, simple security/monitoring, basic assistance, or companionship.
Home robots can operate without constant human control. They rely on a combination of sensors, cameras, and AI-based navigation algorithms to map and understand their surroundings. Therefore, they can avoid obstacles and move safely in and around the indoor environment.

Among different applications of domestic robots, cleaning is the most established segment. For your information, the first vacuum cleaner robot was the Electrolux Trilobite prototype, introduced in 1997. Despite the limitations in navigation, Trilobite was still a groundbreaking invention that paved the way for the modern generations of robotic vacuum cleaners. Later in 2002, Roomba was introduced, and it became the first vacuum cleaner robot that gained widespread commercial success. The model featured sensors that were more effective at detecting obstacles and avoiding stairs, overcoming the weaknesses of the predecessor.
Now, people have a plethora of choices for vacuum cleaning and mopping robots, from well-known brands like iRobot’s Roomba line and Roborock to models from Ecovacs, Eufy, and Xiaomi. Many newer models even integrate AI to improve mapping, avoid obstacles more intelligently, recognize different rooms, and sync with voice assistants, making cleaning experiences feel smarter and more personalized than ever.

Beyond cleaning, smart kitchen appliances also incorporate robotic functions, from machines that automatically prepare ingredients to devices that monitor cooking and adjust settings for better results. For instance, the Thermomix TM6 can chop, mix, steam, and cook following step-by-step guided recipes, or the Moley Robotic Kitchen uses robotic arms to automate entire cooking sequences.
Medical Robots: The Healing Robots
Robotic automation can be woven into care pathways while keeping human professionals firmly in charge. In the modern healthcare setting, medical or medicine robots refer to a broad category of automated machines and systems. The robotic equipment is designed and integrated to extend what healthcare practitioners can do.
In environments where mistakes carry extremely high stakes, especially when they impact not just financial costs but, more importantly, human lives and well-being, medical robots are brought in to improve precision, consistency, and coverage.
Medical robots can play various roles, from surgery to hospital operations and logistics.
Robotic Surgery
In operating rooms, surgical robots act as ultra-steady, ultra-precise extensions of the surgeon’s hands and eyes. They assist surgeons with minimally invasive procedures.
A prime example is the da Vinci Surgical System. Surgical robots use finely controlled robotic arms and high-definition cameras to make tiny, precise movements that human hands alone would struggle to match.
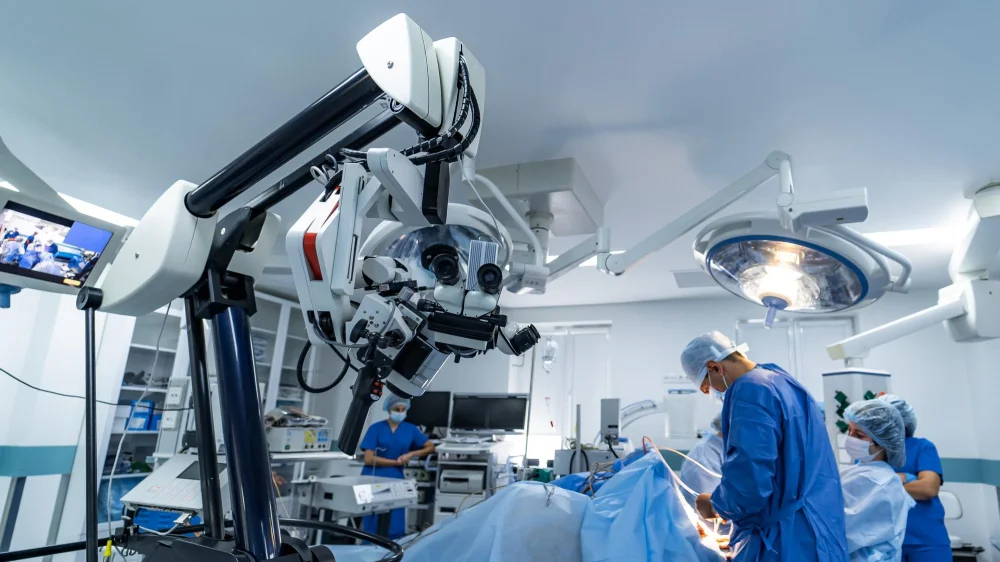
Moreover, these robotic assistants can analyze and translate the surgeon’s hand movements into smaller, controlled motions inside the patient’s body, which can result in smaller incisions, less pain, and faster recovery. Their role is to transform traditional surgeries by providing enhanced precision, stability, and visibility, not to replace surgeons and operate on their own. The invention of surgical robots represents a major step forward in applying technology to medical science, and it gives us good reason to be optimistic about future innovations.
Rehabilitation & Exoskeleton
Robot-assisted rehabilitation and wearable exoskeletons help patients regain movement after strokes, spinal cord injuries, or orthopedic surgeries without requiring constant physical help from other people.
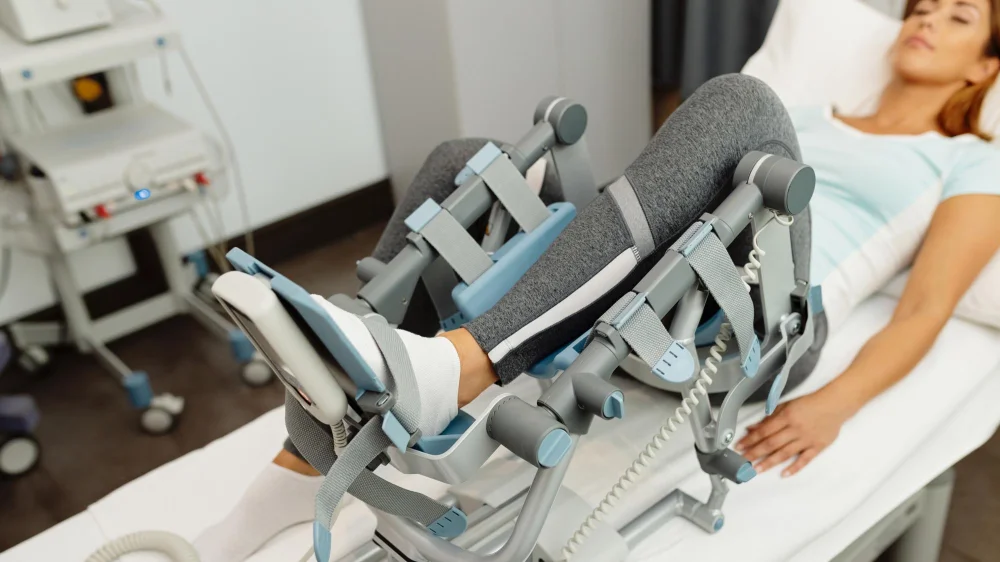

During physical therapy, robotic devices can guide the body through repeatable, controlled motions (E.g., walking, bending, and lifting) while the therapists adjust difficulty levels and track progress. In combination with AI, some systems are able to adapt to resistance, speed, and support levels based on how a patient responds over time.
Assistive & Companion Robots
Some robots are built for emotional and social support rather than medical procedures. Assistive robots remind patients to take medication, drink water, or perform exercises, while companion-like robots provide conversation, entertainment, and cognitive stimulation. Both of them are tasked to support daily routines, reduce loneliness, and supplement the work of caregivers, particularly for elderly patients or those with chronic conditions.
Pharmacy Robots
Robots can offload the most repetitive, high-precision aspects of medication management.
In hospital pharmacies, robotic dispensing systems sort, count, and package pills or prepare intravenous drugs according to digital prescriptions. Robots not only mitigate the risk of human error but also optimize the use of medications. They can locally concentrate therapeutic payload around pathological sites so that they can improve dosing accuracy and minimize waste.
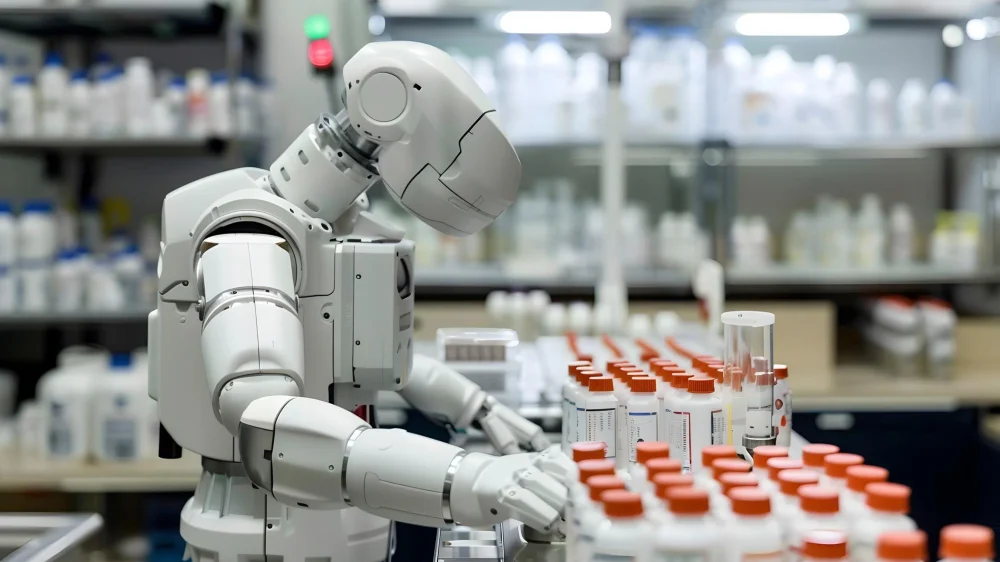

In environments like hospitals or pharmacies where staff always work under heavy pressure, robots can take on high volumes of orders around the clock, speeding up the workflows. On the wards, small autonomous delivery robots transport medication from the pharmacy to nursing stations, so nurses don’t have to leave patients to fetch drugs.
In some outpatient settings, automated kiosks and pharmacy robots fill out prescriptions and label them clearly. Another area where robots prove useful is prosthetics, where a damaged human limb can be replaced with a robotic body part.
Industrial Robots: The Tireless Supporter
If cobots represent a new wave of human-robot teamwork, industrial robots are the long-standing workhorses of modern manufacturing, automotive, and electronics industries. These robots are not visible in everyday life, but almost every product we buy and use has likely passed through a production line supported by industrial robots. Millions of industrial robots are working in factories around the world, and this number is growing rapidly every year.
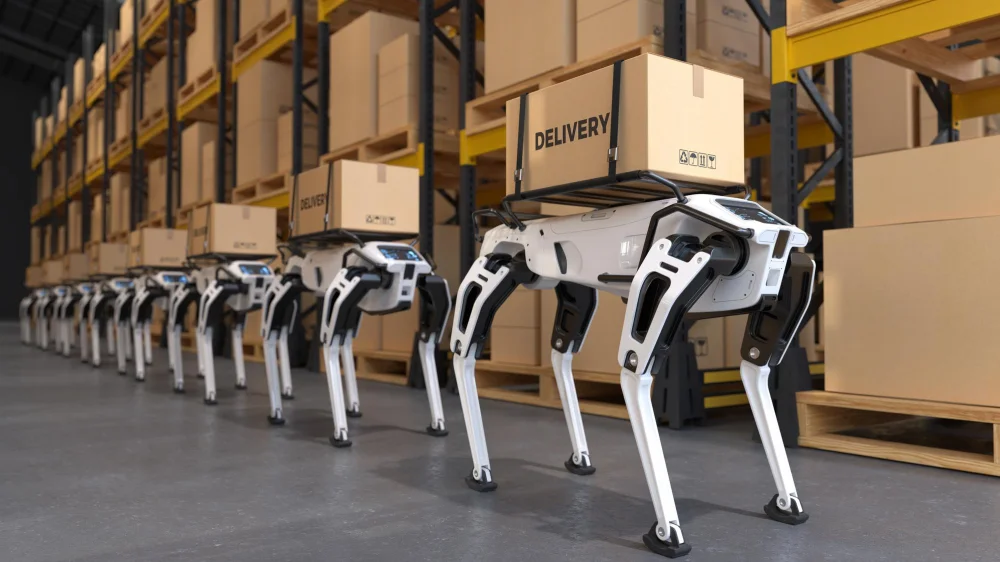

Also known as factory or manufacturing robots, these models are often stationary machines that handle repetitive tasks or jobs with high physical strain. You can picture them on an automotive line: Multi-jointed robotic arms welding, painting, assembling, lifting, or packaging products at a speed and precision humans simply cannot match over long periods of time.
Because they can operate around the clock with minimal downtime, industrial robots help companies maintain consistent quality, meet tight deadlines, and scale production up or down as needed. When combined with human oversight and problem-solving, industrial robots don’t just replace manual labor; they support workers with physically demanding tasks and create safer, more efficient workplaces.
Entertainment Robots: The Fun Companion
As its name suggests, this type of robot is designed for entertaining people. These robots are created to allow people of all ages to experiment with robotics in a fun and intuitive way. Entertainment robots can take many different forms, ranging from simple mechanical toys to sophisticated performers.
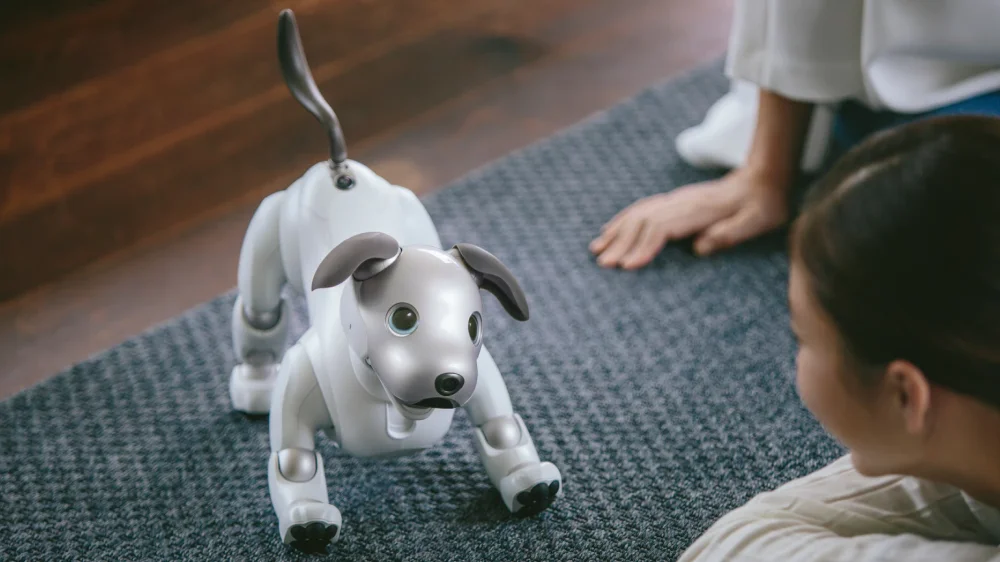

Robotic toys are some of the most visible examples in everyday life: Small, interactive robots that can roll, dance, react to voice commands, or respond to touch. They often come with companion apps or coding modes that let users change behaviors, record movements, or create simple programs, blending play with learning.
Over time, developers aim to make robotic toys more affordable and accessible to a wider audience. A well-known example of a robotic toy is Sony Aibo - a cute robotic dog that can walk, play, recognize its owner, and express emotions through movements and sounds. Or, we have Anki Cozmo – a small, characterful robot with a digital face and expressive eyes that plays games, interacts with special cubes, and can be programmed by kids through a simple application.
Educational Robots: The Teaching Assistant
It is now naturally common to discuss robotics in education. Out of labs and factories, robots are brought to places where people learn: Classrooms, makerspaces, training centers, or even living rooms. In their simplest form, educational robots are interactive, programmable devices designed and used for teaching and learning. They range from wheeled or small robots to robotic arms or toys and humanoid robots.
Let’s take NAO as an example. It is a programmable humanoid robot used in universities, research labs, and some schools for more advanced projects involving human–robot interaction, AI, and social robotics.
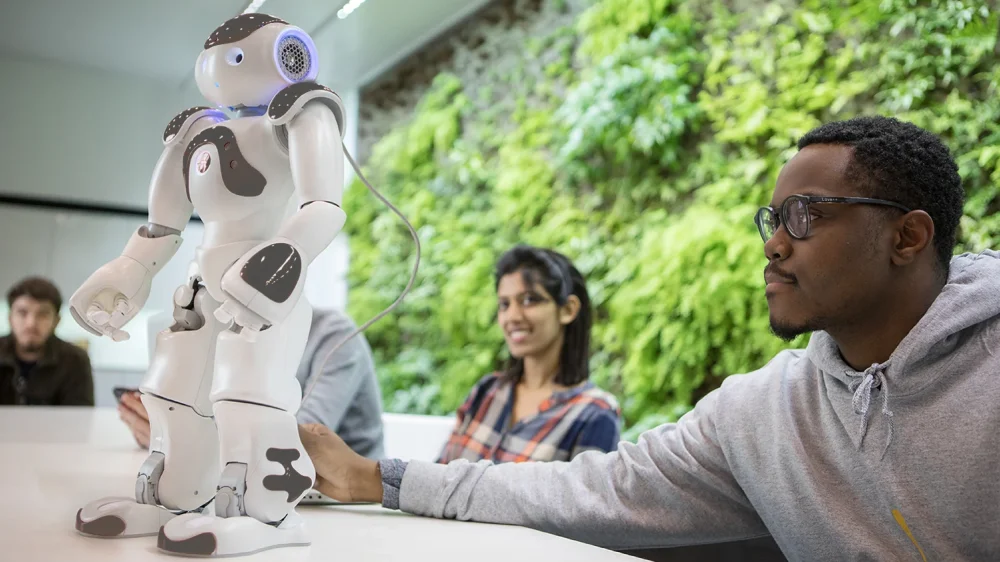

Robots augment teaching by streamlining repetitive tasks, personalizing experiences, and visualizing educational lessons in a more engaging way. For learners, educational robots turn abstract concepts into something they can see, touch, and experiment with. Instead of just reading about algorithms, physics, or problem-solving, students can program a robot to move, react to sensors, or complete a challenge and immediately see what went wrong or right. This direct feedback loop makes learning more tangible and less intimidating and encourages trial and error.
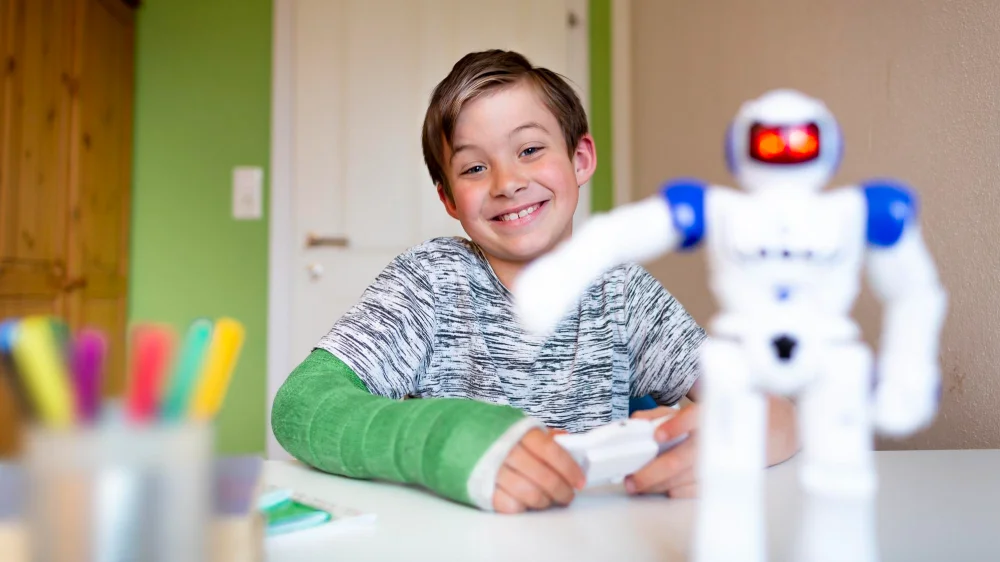

Moreover, autistic students generally find robotics a great assistance tool that helps them learn social cues and engage with the world in a more comfortable way. Because robots behave consistently and reduce the pressure of direct person-to-person interaction, they can make it easier for autistic learners to experiment with communication, turn-taking, and collaboration at their own pace.
Education robotics is not limited to children or formal schooling. They are used in after-school clubs, coding bootcamps, corporate training programs, and hobbyist communities to explore a variety of topics, such as basic STEM and intelligent automation.
Self-Driving Robots: The Automated Transportation
These robots cover everything from small sidewalk delivery bots to full-sized vehicles with advanced driver-assistance systems. They rely on a mix of cameras, radar, lidar, GPS, and AI models to perceive lanes, traffic, obstacles, and pedestrians, then decide how to steer, accelerate, and brake with minimal human input. In practice, most real-world deployments today are still supervised or limited to well-defined areas, but they already hint at how deeply automated transportation could reshape everyday logistics and mobility.
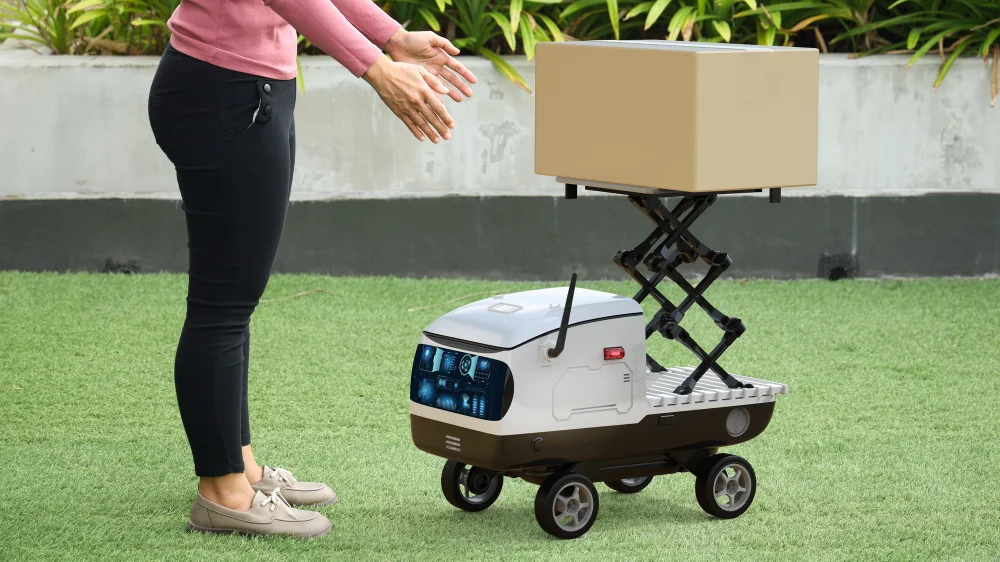

One concrete, real-world example is the delivery robot from Serve Robotics. It is called “Serve.” These small, electric sidewalk robots handle food and grocery delivery in a few U.S. cities, travelling at walking speed on pavements instead of driving on the road. Using cameras, sensors, and onboard AI, they navigate around pedestrians and obstacles, cross intersections, and stop at the customer’s location, while remote human supervisors can step in if something unexpected happens. Serve has completed hundreds of thousands of deliveries for partners such as Uber Eats and 7-Eleven and is scaling toward around 2,000 robots deployed across multiple U.S. cities by the end of 2025.
Tesla is another good example of this area. Its autonomous self-driving cars offer assistive features branded as Autopilot or Full Self-Driving, but they are not fully autonomous: Drivers must stay attentive and ready to take over at any time, and regulations still treat them as driver-assist systems, not driver replacements.
Agricultural Robots: The Sidekick of Modern Farmers
Robotic assistants become the extra hands that can turn farm work from pure physical labor into a mix of field expertise and data-driven decision-making. In this human-robot teamwork, robots handle endless, back-and-forth jobs, while humans choose what to plant, when to harvest, and how to balance yield with soil health and long-term sustainability.
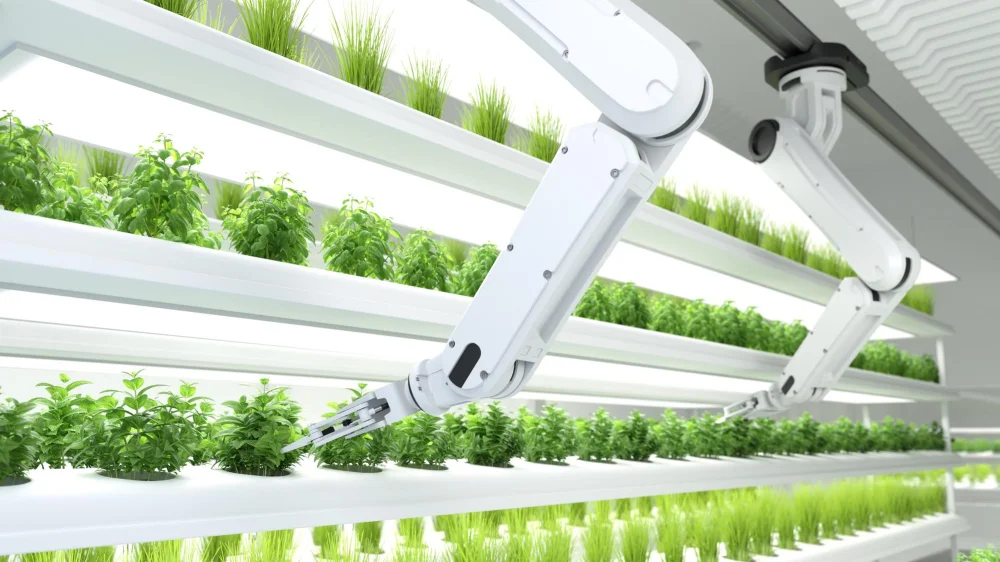

Agricultural robots include autonomous tractors and sprayers, robotic weeders, harvesters, and automated systems for feeding or milking livestock. Using GPS, sensors, and AI, these robots can navigate fields, treat crops more precisely, and collect data on soil and plant health. The result is more efficient, data-driven farming where robots handle the routine passes up and down the field, while farmers focus on strategy, stewardship of the land, and managing their business.
Telerobots: The Distant Operator
This term is short for teleoperated robots. Simply put, telerobots enable participation in a remote location. You can control a telerobot from a distance, usually through a combination of sensors, cameras, and communication links that transmit commands and feedback between the operator and the machine itself.

These robots will not function autonomously; they act as an extension of a human operator to allow humans to perform tasks in places that would be normally dangerous, inaccessible, or too delicate for direct handling. For example, a student recovering at home can still roll into class on a telepresence robot, pivoting its camera to follow the teacher and join group work; a specialist engineer can “walk” a remote factory floor without boarding a plane; an inspector can examine a risky site without stepping into danger.
Final Thoughts
The future of human-robot collaboration is less about replacement and more about partnership. Over time, working and living with robots has become more comfortable. People stop seeing robots as mysterious black boxes or fear machines’ presence in their daily lives. Instead, we learn to work alongside robots and leverage the automation they bring while leaning into the things humans naturally excel at, such as judgment, empathy, creativity, or problem-solving.
As acceptance and familiarity grow, the next logical step of robotics lies in artificial intelligence. AI-driven robots move beyond mechanical precision and start becoming genuinely perceptive collaborators.
For businesses ready to embrace this shift, the challenge lies in designing and implementing AI systems that are reliable, scalable, and aligned with real-world operations. That’s where Orient Software comes in. We help you design and implement the intelligence behind modern robotics, from custom machine learning models and computer vision systems to real-time decision engines.

If you are unsure about your next step in your AI journey, our experts are here to guide you. At Orient Software, we offer comprehensive AI consulting services that go beyond implementation. We help you build a clear strategy, prioritize initiatives, and plan a realistic budget. From identifying the most impactful use cases to selecting the right technologies and building scalable solutions, our dedicated team ensures that your AI investments deliver measurable value. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to optimize existing AI systems, we provide the insights and guidance you need to make confident, informed decisions every step of the way. Hesitate no more and contact us today.