Cloud Computing Programming Languages 101: Learn the Ones Powering Modern Apps
We'll unpack the programming languages developers trust most for developing high-performance applications running on the cloud.
Content Map
More chaptersThese days, it feels like everything is in the cloud. Your photos, emails, entertainment shows, courses, business tools, and even your AI assistants are hosted in the cloud environment. It is true to state that cloud technology has quietly become the digital foundation of our daily lives. Not only individuals, but also startups, scaleups, and enterprises are relying on cloud-based services.
With the growing need for flexible resources, new platforms, and as-a-service offerings, cloud computing is on fire for expeditious adoption and expansion opportunities. Analysts at Gartner now forecast that global public-cloud end-user spending will reach US $723.4 billion in 2025, up from US $595.7 billion in 2024. At the same time, spending on cloud infrastructure services (IaaS and PaaS) is expected to grow more than 20% in 2025. In parallel, over 90% of enterprises report using cloud services in some form, and 89% of organizations say they now have a multi-cloud strategy in place.

While on the subject, let’s take a closer look at what truly powers the transformation of cloud-based services and distributed systems: Code and the programming languages. These languages form the backbone of cloud innovation. They translate ideas into logic, turning the limitless potential of the cloud into tangible, working systems.
Before diving into the best cloud programming languages, it’s worth understanding what makes a language cloud-ready and why some have become the go-to choices for building modern, cloud-native applications.
Key Takeaways:
- Cloud programming languages are not a separate category but refer to any language optimized for building, deploying, and managing cloud-based applications and infrastructures on platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- A good cloud language should balance scalability, speed, portability, ecosystem support, and security while integrating seamlessly with cloud APIs and services.
- Selection criteria include platform support, portability, application type, ecosystem, development speed, security, integration, and community support.
- Python: Simple, versatile, and rich in libraries for automation, AI, and serverless development.
- Java: Object-oriented, stable, and ideal for enterprise-level, data-driven cloud applications.
- Go (Golang): Built for concurrency and performance, perfect for distributed systems and containers.
- Ruby: Prioritizes developer productivity, great for rapid prototyping and CI/CD workflows in cloud environments.
- C#: Integrates tightly with the .NET ecosystem for robust, secure, and scalable Azure applications.
- JavaScript/TypeScript: Powers both front-end and back-end cloud services, especially effective in serverless and event-driven architectures.
What Is the So-Called “Cloud Programming Language?”
In short, cloud computing is defined as the on-demand delivery of computing services, encompassing data storage, databases, analytics, networks, servers, machine learning, web applications, and IT support, hosted over the Internet on a pay-per-use basis, tailored to user needs, and managed by a service provider.
Cloud computing services are implemented and supplied to users in three primary models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Similarly, cloud resources are also classified into three categories: Public and private clouds, and hybrid cloud solutions that fall somewhere between.
Definition

So, what’s a cloud or cloud computing programming language? Let’s be clear. It is not a specific or separate category of language by definition. The terminology refers to any coding or scripting language that is well-suited for developing, deploying, and managing applications and infrastructure on major cloud platforms, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS Cloud), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, Oracle Cloud, and VMware.
Selection Criteria
A certified “cloud programming language” must be the one that balances speed, scalability, and ease of integration across cloud platforms. The right choice for a cloud project depends on several specific attributes that you need to factor in. Here’s what you should consider in a cloud-compatible language:
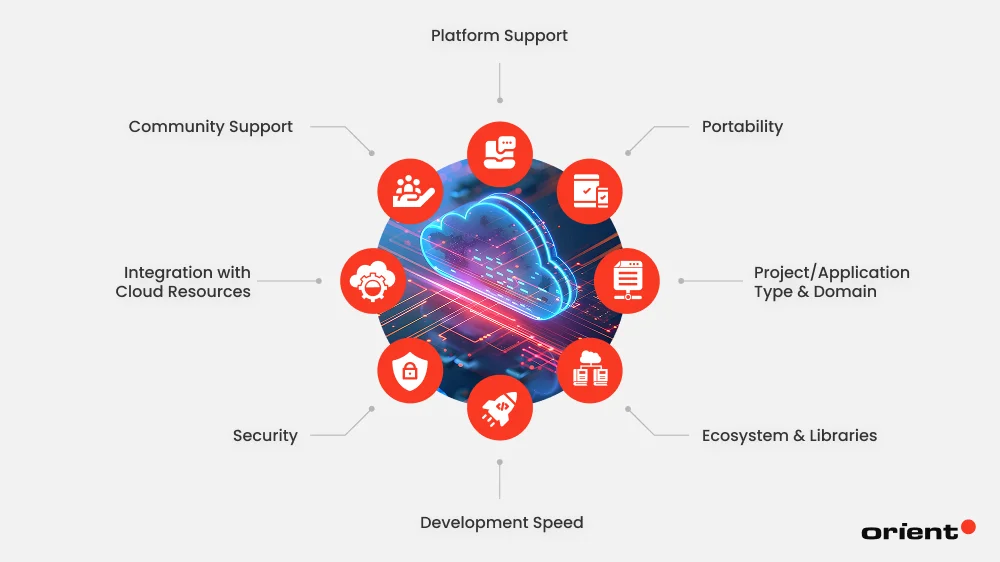
Platform Support
One of the key dynamic elements that helps you filter out the ideal language for cloud computing is its built-in support for cloud technology resources, such as infrastructure tools and frameworks, alongside native compatibility with major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Portability
Since cloud infrastructure is heterogeneous, the language must allow developers to run code consistently across various operating systems, containers, and serverless environments. A portable language helps reduce vendor lock-in and ensures smooth deployment across multiple clouds or hybrid setups.
Project/Application Type & Domain
Knowing what you are building is a primary factor when choosing the best language for your project. This is because different languages shine in different domains. For instance, data-heavy and AI-driven workloads benefit from Python, while enterprise-scale systems might lean toward Java or C#. Matching the programming language to your domain ensures optimized performance and maintainability.
Ecosystem & Libraries
An ecosystem of extensive support libraries and frameworks empowers developers to integrate essential features without having to reinvent the wheel. For example, databases or network security. The more comprehensive and well-maintained the ecosystem, the faster and more reliable your cloud application development will be.
Development Speed
In cloud environments where continuous deployment, frequent updates, and serverless functions are common, dynamic-typed languages that enable rapid prototyping, ease of change, and readability are valuable choices. Python, for example, is a highly approachable language that brings along many libraries to automate cloud setups and accelerate the initial development phase. For more mature and complex projects, compiled programming languages (E.g., Java and C#) might be a better fit.
Security
Aside from robust capabilities, security features are also important, particularly when applications are planned to handle sensitive data. Programming languages with strong security libraries, safe defaults, and mature tooling are often beneficial choices.
Integration with Cloud Resources
Cloud-friendly languages should easily connect with APIs, storage, monitoring, and deployment services. This integration ensures seamless management of distributed systems and efficient use of compute, storage, and networking resources offered by cloud providers.
Community Support
In software engineering, nothing is better than using a programming language backed by a thriving community. Active forums, open-source contributions, and community-driven improvements can make a significant difference in long-term cloud project success.
The Best Programming Languages for Cloud Development

Below are the top programming languages shaping cloud development today:
Python - The All-Purpose Cloud Favorite
Let’s kickstart with one of the most popular programming languages: Python. Released in 1991, the general-purpose programming language by Guido van Rossum has long been the first pick of developers who learn cloud computing. Python earns its place thanks to its clean, simple syntax, easy-to-read code, and enormous ecosystem of libraries. These characteristics make a high-level language like Python an excellent choice for beginners and non-programmers.

In the cloud development environment, Python’s popularity stems from its simplicity and versatility, all within one language. Simple syntax enables Pythonistas to reduce unnecessary complexity and speed up writing code - accelerating development cycles. Meanwhile, this versatile language allows for adapting to any cloud-based use cases, from scripting automation tasks to powering full-scale AI applications in the cloud environment.
In the realm of cloud development, Python’s flexibility shines through its deep integration with major cloud service providers. SDKs such as Boto3 for AWS, Google Cloud Client Libraries, and Azure Software Development Kit for Python make it incredibly easy to automate deployments, manage cloud infrastructure, and build scalable applications. Its lightweight nature and compatibility with serverless platforms like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions also make it ideal for event-driven workloads that need to scale on demand. Beyond that, Python has a strong foothold in building dynamic web pages, APIs, data analysis, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) algorithms. These areas perfectly align with today’s cloud priorities.
Also, developers often use a simile to compare Python to a “Swiss army knife” of languages due to its enormous ecosystem of open-sourced libraries and frameworks like Django, Flask, and Pyramid. Some available tools and solutions are specifically designed for cloud computing technologies, further enhancing Python’s suitability for this domain. Last but not least, its active community also facilitates the easy sharing of extensive knowledge and experience among developers and programmers.
Java - The Enterprise Cloud Powerhouse
Brought into existence by Sun Microsystems, Java is well-known for its WORA (write once, run anywhere) capabilities. Currently, Java is recognized as a classic language used by generations of developers for various types of software development projects, including cloud-based applications.

Java’s object-oriented programming (OOP) approach is designed to build complex and enterprise applications with well-structured, modular code that is more maintainable in the long run. The vast ecosystem of frameworks, like Spring Boot and Hibernate, supports enterprise-level development for data-driven web services and microservices architectures.
Meanwhile, Spring Cloud provides a suite of tools for building resilient, cloud-native applications, handling key concerns like configuration management, service discovery, load balancing, and distributed tracing. With the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), programs are platform independent of the underlying OS, and this makes Java highly portable for cloud deployment.
Go (Golang) - The Cloud-Native Expert
In regard to a cloud programming language with scalability, Go or Golang stands out as a modern option. Developed by Google in 2009, Go was an open-source language purpose-built for the modern cloud era. Its design emphasizes speed, concurrency, and simplicity. Therefore, Go becomes a natural fit for distributed systems, containerized services, and large-scale cloud infrastructures.
Golang’s static typing system helps minimize runtime errors, making Go-based applications more secure and reliable. With built-in concurrency through goroutines, developers can easily design multi-threaded applications that fully leverage multi-core CPUs and cloud resources.
Go also comes with a robust standard library that simplifies tasks like networking, encryption, and building web servers. Combined with efficient memory management and a lightweight runtime, Go delivers the high-speed performance and low overhead needed for modern cloud infrastructures.
Ruby - The Go-to Lang for Rapid Prototyping
Created in the mid-1990s by Yukihiro “Matz” Matsumoto, Ruby was designed with developer happiness in mind. The coding language was designed with an emphasis on simplicity and developer productivity over verbosity or rigid syntax. Oftentimes, Ruby is cited for web development. Coupled with its powerful framework, “Ruby on Rails”, this programming language is highly recommended for developing cloud-native applications.

While Ruby may not be as dominant as it once was, it remains a preferred language in the cloud ecosystem, especially for rapid application development and prototyping. Featuring a clean syntax, Ruby enables developers to write concise and readable code while offering an object-oriented programming paradigm.
In the cloud development environment, Ruby continues to thrive thanks to its easy deployment and scalability. Popular platforms like Heroku, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and Google Cloud Run offer seamless integration with Ruby and Rails applications, allowing developers to move from concept to production quickly. Its rich collection of gems (pre-built libraries) simplifies everything from API integration to authentication, helping teams build robust cloud applications with minimal overhead.
Ruby also aligns well with modern DevOps practices. With strong support for continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD), developers can automate testing, updates, and rollouts effortlessly. Combined with its vibrant global community, Ruby guarantees that developers can access abundant resources, tutorials, and open-source contributions. This makes it a reliable choice for teams prioritizing speed, flexibility, and maintainability in the cloud.
C# - The Backbone of Microsoft Azure
Originally developed by Microsoft in the early 2000s, C# remains one of the most powerful and reliable languages for cloud app programming tasks. Its seamless integration with the .NET ecosystem makes it a natural fit for developing and deploying services on Microsoft Azure, where it excels in performance, security, and scalability.

With frameworks like ASP.NET Core, developers can create high-performance APIs and microservices that run efficiently across platforms, while Azure Functions make it easy to build serverless applications using C#. The language’s strong typing system and asynchronous programming capabilities also help ensure stability and responsiveness in large-scale, distributed systems.
C# continues to evolve with each .NET release, improving its compatibility with containers, Kubernetes, and multi-cloud environments. For teams already invested in the Microsoft stack, C# offers a familiar yet modern foundation for building enterprise-grade cloud solutions that can grow alongside business needs.
JavaScript/TypeScript - The Full-Stack Cloud Enabler
Back in 1995, JavaScript was created as a scripting language for web browsers. The language was never meant to power the cloud. It began as a lightweight method for making static web pages interactive. Fast forward nearly three decades, and JavaScript has transformed into one of the most ubiquitous and versatile programming languages on the planet. Once confined to the browser, JavaScript has evolved into a full-stack powerhouse that now plays a vital role in cloud computing.

Thanks to Node.js, developers can now build backend services, APIs, and real-time cloud applications using the same language they use on the front end - JavaScript. Its asynchronous, event-driven nature makes it exceptionally well-suited for serverless and event-based architectures, where scalability and responsiveness are key. Cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud all offer first-class support for JavaScript in their serverless environments.
For large-scale, production-grade systems, TypeScript, a superset of JavaScript, adds static typing and improved maintainability, making it ideal for complex, distributed cloud environments. Combined with modern frameworks like Express.js, NestJS, and Next.js, JavaScript and TypeScript empower teams to create cloud-native, full-stack solutions with unmatched speed and flexibility.
Wrapping Up
These six programming languages are among the top cloud-friendly options to consider. If you need professional support, don’t hesitate to contact Orient Software. We are an outsourcing powerhouse based in Vietnam. We have been working with hundreds of global partners and have successfully delivered 200+ projects. Aside from technical consultancy, you can delegate the entire development process to our team or collaborate with us to augment your team with elite talent. Explore our services to discover the ideal solutions for you and consult with our experts.