What Is ‘AI Washing’ and How Can You Avoid It?
Learn what AI washing is, why it matters, and how to avoid misleading claims about artificial intelligence in this concise guide for businesses and consumers.

Content Map
More chaptersSince the release of ChatGPT in November 2022, interest in generative artificial intelligence (AI) technology has skyrocketed.
More companies are integrating generative AI into their products and services with the hope of enhancing their capabilities and gaining a competitive edge. Venture Capitals (VCs) are also ramping up investment in generative AI startups, investing 3.9 billion USD across 206 deals in Q3 2024.
Despite the hype surrounding generative AI, regulators, investors, and customers are starting to scrutinize companies that falsely claim to use or exaggerate their use of the technology.
In this article, you will learn about what AI washing is, its legal and ethical implications, and the industry’s response.
Key Takeaways:
- AI washing occurs when companies make false claims about the use of AI in their products and services.
- The motivators behind AI washing are to gain an unfair competitive edge, increase sales, and attract more investors.
- Working with a reputable AI development services company like Orient Software can help you use and promote AI ethically.
What Is AI Washing?
Definition and Forms of AI Washing
AI washing is when a company falsely claims to use AI in its products and services. It also refers to when a company over-exaggerates the capabilities of its AI technology. Both forms of AI washing are designed to align a product or service with a current trend – that being AI – to make it more desirable.
Many companies have been accused of partaking in AI washing. In April 2014, it was reported that Amazon Fresh’s ‘Just Walk Out’ technology relied on 1,000 workers in India to confirm about three quarters of all transactions manually. The company responded to the claims by stating that the workers were reviewing the system that powers the technology.
Coca-Cola was also accused of AI washing when it introduced a new drink called ‘Coca-Cola Y3000’. The company claimed that it used AI to create the new flavor but provided no concrete evidence as to how it did so.

Motivations Behind AI Washing
Companies may partake in AI washing intentionally or unintentionally. Those who do it intentionally may gain an unfair competitive edge, mislead customers into buying their products and services, and mislead investors into providing more funding for their businesses.
Companies that unintentionally engage in AI washing may do so due to a false understanding of how AI works. For example, a company may assume that their new chatbot is powered by AI but is in fact a traditional rule-based chatbot.
Why Is AI Washing Problematic?
There are many reasons why AI washing is problematic. Customers may overpay for products and services that don’t deliver on their purported AI capabilities. As a result of being disappointed by the results of a misrepresented product or service, customers may become increasingly distrustful of AI in general.
AI washing is also problematic for the investor world. Companies that falsify their use of generative AI make it harder for investors to identify legitimate investment opportunities. In addition, investors can take advantage of AI washing for their own personal gain.

What Are the Legal and Ethical Implications of AI Washing?
The advent of AI washing has led to many high-profile legal cases and raised questions about the ethical implications. These events have triggered a strong response from industry experts and regulators.
Legal Implications of AI Washing
Companies that partake in AI washing are beginning to feel the pinch from regulators. Here are a few examples of relevant rulings from around the world.
Delphia and Global Predictions (USA)
On March 18, 2024, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) made settlement charges against two investment advisors, Delphia (USA) Inc. and Global Predictions Inc. Both companies made false and misleading statements about their leverage of AI and its achievable outcomes.
Delphia publicly claimed that it was using AI and machine learning (ML) – algorithms that reveal hidden patterns within datasets – to analyze client data and drive investment decision-making. Global Predictions made similar false claims, promoting itself as the “first regulated AI financial advisor.”
Codeway (UK)
In the UK, the Advertising Standards Authority (ASA) made a ruling against Codeway, creator of the AI photo enhancer app Pixelup. The ruling was about the distribution of a misleading paid Instagram ad.
The ad displayed a black & white picture of a person split into two separate images. The image on the left was extremely blurry, while the image on the right was sharper and clearer. Underneath the ad was the text “Enhance your photos with AI.”
ASA concluded that the ad was misleading, as Codeway did not provide evidence that the image on the left was genuine and had not been distorted to exaggerate the app’s efficiency.
Ethical Implications of AI Washing
Beyond the legal ramifications, AI washing has ethical implications. Customers and investors are often confused by what AI does, how it works, and the tangible benefits for users.
This problem is exasperated by the fact that many companies lie about the originality of their AI integrations. Some boast about having “unique” AI models. But in reality, they all draw from the same underlying AI models to power their products and services. The only difference is how they promote themselves.
When so many companies tout their own AI capabilities, it can confuse and frustrate customers and investors. They have a harder time separating genuinely innovative companies from cheap imitations.
How Is the Industry Responding to AI Washing?
AI washing is still a relatively new phenomenon. The latest AI capabilities and rulings against companies that partake in AI washing are new. So, the market is still adjusting to this emerging reality.
Unfortunately, many customers and investors are inexperienced in detecting AI washing. They lack the knowledge and resources to scrutinize companies that make false or misleading claims about their AI capabilities.
This confusion is compounded by the fact that so many companies claim to be AI-powered but don’t fit the bill. A 2019 study by MMC found that only 1,580 out of 2,830 startups in Europe accurately fit the description of being AI companies.
One way companies can combat AI washing is to follow industry best practices when promoting their AI capabilities.
What Are Some Best Practices to Follow When Adopting AI Capabilities?
Organizations (E.g., the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the United States) are aiming at companies that make misleading AI claims.
For this reason, companies should be honest about their AI capabilities. Not just to avoid legal retribution but also build trust with consumers and investors. Fortunately, there are ways to promote your AI capabilities ethically.
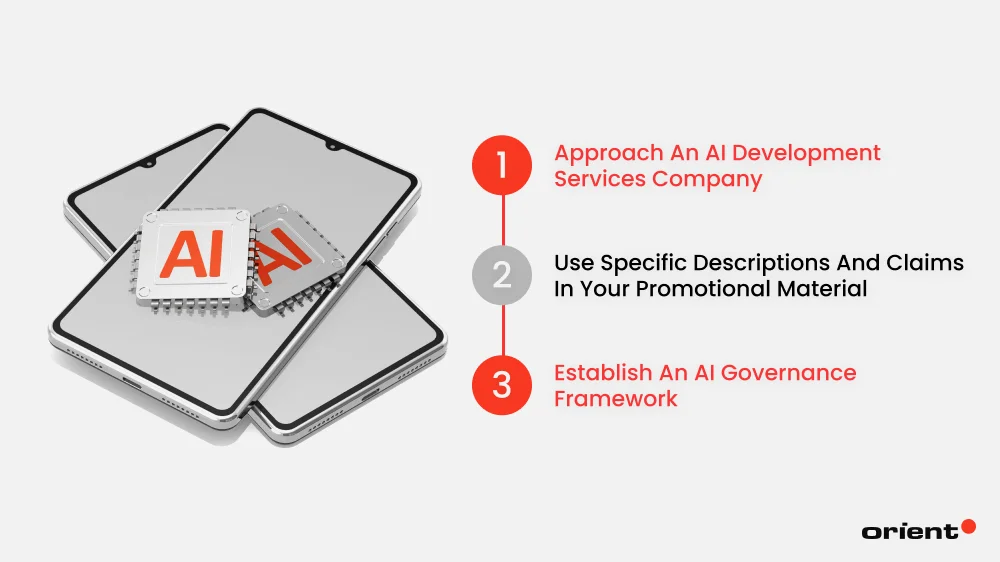
Here are some best practices to follow when adopting and promoting your AI capabilities.
Approach an AI Development Services Company
Most companies that embrace AI do so with the help of an artificial intelligence development services company.
These companies specialize in the development, deployment, and maintenance of AI products and services. They use advanced tools like natural language processing (NLP) and deep learning to create AI products that help boost efficiency, security, and revenue growth.
A company like Orient Software offers end-to-end AI development services. From consultation to implementation, we provide AI solutions that integrate seamlessly with your legacy systems and business processes. And with zero migration issues.
We also uphold the highest standards for ethics in AI. Our data scientists will explain how your AI solution works and the outcomes it can achieve. Your business can then use this information to promote your AI capabilities accurately.
Use Specific Descriptions and Claims in Your Promotional Material
Most accusations of AI washing occur when a company is not transparent about its use of AI. The more guesswork that customers and investors must do, the less likely they are to believe your claims.
How does your business avoid using vague descriptions and generalized claims? Focus on the measurable outcomes your AI capabilities can deliver. Then, describe in detail the process you go through to achieve those outcomes.
Siemens uses AI to predict equipment failures before they occur. The company uses specific data and evidence to support its claims. Their work on AI dates back to the 1970s, and they have over 1,400 experts around the world. These claims are measurable and easy for customers and investors to believe.
Establish an AI Governance Framework
An AI governance framework consists of rules, processes, and guidelines. It is designed to help companies deploy and use AI ethically and responsibly.
To establish an AI governance framework, consult an AI governance services company. They can help you create an AI program to help reduce risk and keep you ahead of all regulatory requirements.
An AI governance services company can involve every department in the drafting process. By understanding how AI will impact their position and workflow, each team member will be on the same page about how they will use and promote AI in your business.
Avoid the AI Washing Trap
AI washing is a major threat to the business world. Companies that make misleading AI claims threaten to erode consumers’ and investors’ trust in AI start-ups. Also, established companies that embrace AI ethically will have a harder time separating themselves from bad actors.

To avoid the AI washing trap, work with a trustworthy AI development company. Orient Software has expertise and hands-on experience in a wide range of AI fields, including generative AI and predictive analytics.
Contact us today. Discover how our AI development services can help your business gain a competitive edge.






