Artificial Intelligence (AI) seems to be the talk of the tech world in 2025. This year has witnessed the rapid AI adoption from large, well-known organizations across almost every sector:
- In consumer electronics, Samsung has partnered with Google Cloud since 2024 to bring Galaxy AI and incorporate numerous innovative features, such as circle to search, real-time call translation, keyboard with translation support, and more.
- Regarding software, Adobe’s Firefly, a suite for generative AI design tools, offers users a centralized platform for generative AI features.
- The automotive industry isn’t an exception to rapid AI adoption. BMW Group uses AI in its manufacturing plants for quality control and predictive maintenance (e.g., analyzing component images in real-time to detect defects).
It is only natural that businesses use advanced AI technology to gain a competitive advantage. In today’s article, we’ll uncover how this tech enhances and empowers business management and how it can benefit every industry.
Key Takeaways:
- Once performing simple, low-level tasks, AI has now become the backbone of innovation in business management.
- AI does more than generate responses to specific questions. The technology streamlines operations, automates tasks, and provides important insights and data for decision-making.
- AI is present in every aspect of business management, from human resources, marketing, and sales to product development. It is no longer a faraway, sci-fi concept, but has been applied in the real world by multi-national businesses.
- As powerful as AI is, it still faces challenges and risks regarding data quality, security, and privacy.
The Growing Role of AI in Business Management

AI’s beginnings are humble. It began as a low-level, background assistant, performing specific and repetitive tasks. Think of spell checks and grammar corrections in Microsoft Office. These tasks are specific and rule-based, representing “narrow AI” – an AI system with a limited scope, designed to do particular or closely-related tasks. Other examples of very early AI capabilities include:
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems: Remember those voice guidance “press 1 for sales, press 2 for support”? These phone systems used simple AI decision trees to guide callers, an early automation in customer service that utilized interactive voice response.
- Even in the early 90s, the system was able to filter spam emails thanks to early AI models like Bayesian classifiers. This is also an example of machine learning (ML) in everyday life.
- During its early stages, AI was already used to assist and enhance decision-making. For example, banks were using AI to detect anomalies in credit card activities – much faster and efficient compared to manual checking. The technology is also used to execute trades based on signals and patterns – a foundation for algorithmic trading.
- Healthcare during the early days utilized AI to support medical diagnosis. Systems like MYCIN (1972) recommended antibiotics based on symptoms.
Needless to say, AI has come very far ever since those early days. According to a Gartner survey, nearly 8 in 10 corporate strategists believe AI and analytics will be key to their success in the next two years. AI-powered businesses will be the norm.
The Benefits of AI in Business Management
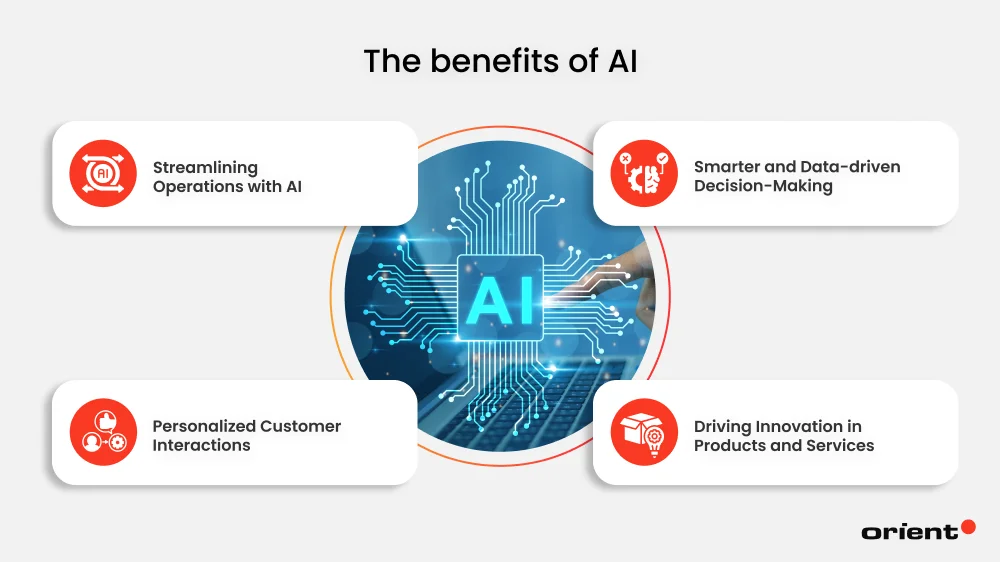
Streamlining Operations with AI
AI’s ability to collect and analyze data gives it unprecedented power to streamline operations.
- Based on sales history, trends, and social statements, AI helps businesses optimize stock levels and prevent overstocking or understocking, predicting demand more accurately.
- AI processes real-time data from IoT devices to increase visibility into their operation, reducing unwanted disruptions and achieving large cost savings. This also allows the company to do proactive maintenance by analyzing sensor data.
- Compared to humans, AI-powered vision systems catch product defects much faster and accurately.
- AI-driven robotic process automation (RPA) takes over repetitive tasks like data entry or report generation, speeding up tasks and cutting down processing time.
- By coordinating tasks across teams and predicting bottlenecks, AI streamlines complex workflows to ensure smooth operation.
Smarter and Data-driven Decision-Making
AI-powered tools allow teams to make faster and more confident decisions. Beyond simple data gathering, AI studies historical data, spots trends, and predicts future outcomes.
Risk management is a crucial part of the decision-making process, especially when there are complex risks involved, like fraud or cybersecurity threats, in the fintech sector. AI can quickly detect anomalies and flag them so organizations can take timely action.
Lastly, utilizing natural language processing (NLP for short), a subfield of AI, enables data-backed decisions by understanding human language, supporting sentiment analysis, and more.
Personalized Customer Interactions
AI doesn’t have to be solely about numbers and analyzing data. It is a great tool for enhancing customers’ experience and satisfaction. Virtual assistants or chatbots, for instance, can deliver instant and personalized responses at all hours of the day. AI systems can also be based on customers’ past behaviors to deliver personalized recommendations. Think of Netflix’s algorithm and recommendation engines – it suggests content based on users’ viewing habits to keep them entertained and engagement high.
Driving Innovation in Products and Services
AI is often used to kickstart ideas. Its ability to generate texts, images, and videos has been of great use for many. However, for true innovation to take place, it takes more than idea generation.
The technology can be used to develop further. Using multiple AI techniques (machine learning, NLP, etc.), users can refine current ideas, combine or restructure pre-existing ones, or even ask AI to simulate a complex scenario and identify solutions for them. Its ability to generate and refine ideas is almost endless and should be explored further, as it has the potential to give businesses a significant competitive advantage.
Applications of AI in Business
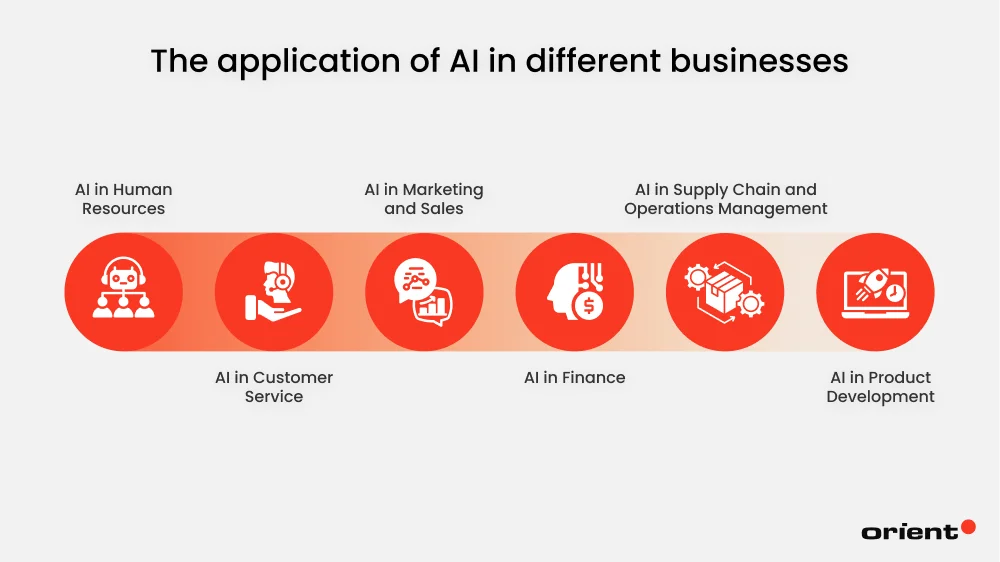
AI in Human Resources
An improved recruitment process plays a major role in a company’s overall operational efficiency. It is reported that more than 67% of employers are using automated systems to filter applicants, as AI systems have become essential for managing the sheer volume of job seekers.
- AI is utilized throughout the recruitment cycle. It streamlines every process, from screening to onboarding.
- AI can promote more unbiased hiring, as it minimizes unconscious bias and supports diversity in recruitment.
- AI’s predictive analytics enables HR teams to identify turnover risks and future talent needs. From there, teams can develop retention plans or succession strategies.
- Once a new employee is onboarded, AI can handle tasks related to the process and even suggest training documents.
- AI-powered tools provide companies with actionable insights to support better goal setting and fair reviews.
AI in Customer Service
Chatbots are not a new concept, as they emerged as early as the 1960s. However, traditional chatbots often rely on pre-written scripts and templates to respond to customers’ inquiries, often leaving them frustrated at these “canned” responses.
Modern chatbots harness the power of large language models (LLMs) and deep learning to generate much more human-like responses that are coherent and contextually relevant. This allows AI to automatically respond to frequently-asked questions, track orders, and/or send notifications. The tool frees up time so team members can handle complex tasks that need human insights.
AI in Marketing and Sales
Data in marketing and sales is invaluable, and using AI is exactly how businesses can transform mountains of data into actionable insights.
- Manually gathering data and then analyzing it takes long labor hours that sometimes go beyond human capacity. AI, however, simplifies this task by gathering data on market trends and consumer behavior to come up with tailored marketing campaigns for the targeted customers. This leads to personalized content strategy, social media strategy, and more.
- If you and your team members are unsure if a campaign works or not, AI will do the testing for you. Continuous A/B testing paired with real-time performance monitoring ensures every marketing dollar is well spent. AI also gives managers clear reports to see which channels drive results and where to invest in next.
- In sales, the representatives need to constantly work on removing bottlenecks from the sales pipeline and have a personalized approach to customers. All these processes can be streamlined with the use of AI.
- AI technology is extremely powerful when it comes to lead prioritization and providing companies with comprehensive reports, giving team members a clear idea of where to direct their efforts and which areas can be improved.
AI in Finance
Finance is one of the most heavily regulated sectors. Moreover, they deal with mountains of data on a daily basis. Managing both compliance and data can be daunting; that’s why AI has been harnessed in the industry very early on. Modern AI technology allows companies to manage money and sustainable growth.
- Continuous data collection, automatic analytics, and predictive alerts give companies instant visibility into performance, enabling timely and informed responses.
- AI-powered systems constantly process data that comes in and identify suspicious transactions and potential risks, safeguarding the company’s and customers’ data.
- AI-powered robo-advisors guide investment decisions using market data and financial goals to optimize returns.
- AI tools are used to evaluate borrower data to streamline data scoring and reduce default risks.
- Teams use AI to assist in regulatory compliance, whether it is managing complex documents, logging audit trails, or assessing compliance risks.
AI in Supply Chain and Operations Management
The application of AI in supply chain and operations is as diverse as it is transforming:
- AI enables businesses to predict the maintenance needs of equipment, minimizing expensive downtime and disruptions.
- To improve supply chain efficiency, managers and business leaders use AI to forecast demand and plan accordingly.
- AI isn’t used solely for internal business processes. It also supports informed decisions regarding vendor and supplier reliability and risks.
- For potential risks, AI supports teams in the assessment and contingency planning.
AI in Product Development
To thrive in a constantly evolving market, a company’s products must evolve too. Nonetheless, keeping up with the ever-changing market pace can be challenging, as it can take months and months to complete the very first iterations of the first product.
Technology has cut down this timeframe significantly. Artificial Intelligence not only generates ideas for you to kickstart the next product development project, but it can also create a prototype or mock-up in a few hours. It’s important to note that AI does not replace human insight and creativity, but it merely empowers them. A strong product innovation needs human supervision and input. Once the prototype is introduced for user feedback, AI is a great tool to analyze user sentiment and suggestions for the next steps.
Real Life Examples of AI in Business Management
We learn more from examples, so let’s take a closer look at how giants in the field use AI technology in their day-to-day business management.
Pfizer

Pfizer Inc. is a prominent American multinational corporation specializing in pharmaceuticals and biotechnology. It is among the biggest and most recognizable pharmaceutical corporations in the world.
The organization uses AI for a multitude of applications.
- Pfizer is an early adopter of AI in drug discovery. By using ML and NLP to accelerate the traditionally long and costly process, the company is able to analyze massive data sets to uncover intricate links between symptoms, diseases, and underlying biology.
- AI is integrated into clinical development, where AI technology automates report generation and documentation for regulatory compliance, cutting time to market even shorter.
- The pharmaceutical company plans to use AI to print labels (the piece of paper inside your medicine box) that are highly accurate and updated with the most recent changes.
Barclays

Dating back to 1690, Barclays is a major multinational bank with its headquarters in London, England. Even though it is a large and historical financial institution in the world, Barclays has been harnessing AI to modernize operations.
- The organization partnered with Microsoft to deploy Microsoft 365 Copilot to over 100,000 employees worldwide. The AI tool assists in content search and HR inquiries while also providing a dashboard for key updates and resources. The integration has saved employees valuable time spent on navigating multiple systems.
- Barclays uses machine learning-based workload automation and predictive analytics to manage IT operations at scale. AI also minimizes service disruptions and improves system reliability through predictive maintenance and automated alerts.
United Parcel Service

The multinational logistics and technology firm United Parcel Service (UPS) runs one of the biggest integrated networks for supply chain management and international package delivery. As the company needs to manage millions of moving packages on a daily basis, AI helps the company streamline logistics while cutting costs and supporting sustainability goals.
- UPS has developed ORION (On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation), an AI-powered system that analyzes massive datasets on traffic, weather, and delivery priorities.
- ORION aims to create the most efficient roads for drivers, but in a dynamic way by adjusting routes mid-day to avoid traffic jams or accommodating last-minute changes.
- The AI system forecasts delivery volumes and anticipates surges during high-demand periods (e.g., holidays). This proactive approach helps the company prevent bottlenecks.
Challenges and Risks of AI Adoption in Business Management

Impact of Data Quality on AI Outputs
AI is only as good as the data you feed it. It will reflect the quality of the dataset back to us – after all, the datasets are the foundations that build AI.
A flawed and incomplete dataset can cause numerous problems. For example, AI may produce a biased response by only returning results where doctors are males and nurses are females.
More importantly, a poor dataset significantly impacts the decision-making process.
- AI may be confused by outlier datapoints, mistakenly identifying them as signs of failure and even triggering the maintenance process, wasting precious resources. This can be especially harmful in manufacturing or logistics.
- Incomplete information makes it almost impossible for AI to generate actionable insights. It’ll be difficult for the AI model, for example, to return accurate market trends without information on customer behavior, preferences, or sales history data.
- AI hallucination may occur, where AI produces information that isn’t real or accurate. In simple terms, it “sees” or generates patterns and details that don’t actually exist, leading to outputs that sound convincing but are ultimately incorrect.
Risk of Intellectual Property Infringement
Ever since the astronomical rise of Generative AI, there have been multiple concerns regarding the risk of AI copyright infringement. There are two types of common infringements:
- Infringement during the training process of an AI model, as it is often trained on large datasets that include existing copyright works.
- The production and distribution of AI-generated outputs that are replicas of works protected by copyright constitutes infringement.
The usage of trademarked or copyrighted data without consent can influence every future output. Proposed regulations regarding how to govern AI are still unfolding, while major lawsuits against AI copyright infringement are also taking place.
Privacy And Security Concerns
Data security in AI has been an ongoing concern. AI systems are susceptible to cyberattacks, as they often are attractive targets for malicious attackers. After all, AI constantly requires massive datasets that may include sensitive information like health or financial data, and using that data to create user profiles for targeted advertising or other purposes without explicit consent. Data breaches can expose such sensitive data.
With the rapid growth of AI comes high expectations from customers for businesses to maintain high standards regarding privacy, security, and ethics.
High Operational Costs
AI is a powerful tool, but it does come with a high upfront investment. Many businesses consider this to be a significant hindrance.
- First, businesses need to invest in collecting, labeling, storing, and securing large datasets to train AI effectively.
- Next, they need to invest in powerful hardware or cloud platforms that can handle AI workloads, driving up infrastructure costs.
- Hiring skilled AI professionals is expensive, as the supply is limited while the market demand is high.
- Training custom AI takes time and involves significant R&D costs.
- After the training is completed, for AI to bring true value to the business, it must integrate with existing tools like ERP, CRM, and databases. This process can also be costly due to legacy systems modernization as well as legal costs.
- Due to the multitude of AI data privacy and security risks, the company needs to ensure AI’s transparency, fairness, and legal compliance, adding extra costs to operational and legal fees.
- AI requires continuous monitoring, retraining, and updating to maintain performance and reliability.
Best Practices to Implement AI in Business Management (from an Expert’s View)

Implementing AI doesn’t simply influence the technical aspect of an organization. It requires deep, fundamental changes in a business to realign its goals, resources, and long-term vision.
Start with an AI Readiness Check
Implementing AI requires significant time and effort, so make sure your organization is ready for it. Here are the checklists to consider whether you are ready to adopt it or not.
- Consider how effectively AI, data platforms, and analytics are used across departments.
- Does your digital infrastructure support seamless, standardized data flow?
- Are your development teams and innovation processes strong enough?
This assessment helps identify gaps, align stakeholders, and set the foundation for long-term AI success.
Perform a Data Audit
As we’ve mentioned earlier, AI does reflect poor data quality. A data audit helps you:
- Identify all data sources (e.g., customer, sales, and financial systems).
- Ensure accuracy, consistency, and completeness of existing data.
- Remove data silos and improve accessibility across departments.
Don’t forget Ethics in Your Frameworks
Never put AI ethics as an afterthought. Always include it in your AI strategy from the very first day. Have meetings to define clear standards for:
- Data privacy and security
- Fairness and bias prevention
- Algorithmic transparency
Strong data governance earns you trust from customers and team members, prevents compliance risks, and safeguards your organization’s reputation. If you are ever unsure how to proceed with these steps, don’t hesitate to reach out to professionals.
Select the Right AI Tools
AI entails a number of sub-technologies, like ML, NLP, or RPA. Selecting the right tools that fit your long-term goals can make or break the project. We recommend testing the tools on a small scale before a full rollout to minimize risks. Here is a quick note on how to choose the different AI tools.
- Machine learning (ML) for predictive insights and automation.
- Natural language processing (NLP) for understanding human language.
- Robotic process automation (RPA) for streamlining repetitive tasks.
Strengthen AI Teamwork
AI tech alone doesn’t bring value to the company – you need the right talents to implement it well. Sit down with the tech team to identify and close skills gaps in areas like ML, data science, and engineering.
- After you’ve identified the gaps, upskill existing employees through training.
- Hire new talent with specialized AI expertise. Encourage collaboration across teams so AI efforts align with broader business goals.
Include Employees in Your Journey
AI adoption is as much about people as it is about technology. To truly make the most out of what AI can offer, it’s important to foster a culture that embraces technology and innovation.
- Clearly communicate your AI vision and how it benefits employees.
- Cultural readiness ensures that your AI strategy doesn’t just exist on paper. It thrives in practice.
Parting Thought: The Future of AI in Business Management

AI isn’t a passing trend; it is here to stay. The tech is quickly becoming a must-have for any business that wants to stay ahead. It is true that it takes time and effort to implement it right, but the payoff is worth it.
If you’re ready to bring AI into your business but don’t know where to start, Orient Software can help. With over 20 years of experience, we know how to turn ideas into real, working solutions that make an impact. Don’t hesitate and contact Orient Software today!